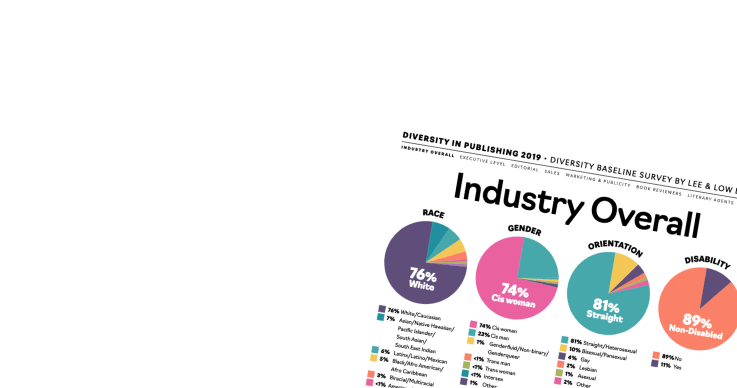
Discussion about diversity in books, at least around here, is often focused on the US market, but the challenges we face regarding diversity here in the United States don’t start and end within our borders. Many countries around the world find themselves struggling with the same growing gap between who is represented in their literature and who their citizens actually are.
Discussion about diversity in books, at least around here, is often focused on the US market, but the challenges we face regarding diversity here in the United States don’t start and end within our borders. Many countries around the world find themselves struggling with the same growing gap between who is represented in their literature and who their citizens actually are.
The international scope of these problems presents us with a unique opportunity to learn from each other and to share knowledge. What works? What doesn’t? What else can we try?
In April 2015, a writer development agency in London called Spread The Word released a comprehensive 44-page study about Black and Asian writers and publishers in the UK marketplace. Supported by  the Arts Council of England, the study delved deep into the experiences of minorities in all aspects of publishing, from acquisitions to literary festivals to creative writing degrees. Here are six important points from that study that I think we can learn from:
the Arts Council of England, the study delved deep into the experiences of minorities in all aspects of publishing, from acquisitions to literary festivals to creative writing degrees. Here are six important points from that study that I think we can learn from:
- New entry-level programs to increase diversity are not enough. For publishers that are serious about increasing diversity in their workforce, entry-level diversity programs must be established in combination with a deeper look at company culture at all levels. Companies should compare pay, retention, and promotion rates of white and non-white staff, suggests Rare Recruitment’s Raphael Mokades: “If you do that rigorous analysis and…you find that BAME [Black, Asian, and Minority Ethnic] people are leaving more quickly or taking longer to get promoted, then you have one of two issues: either all the BAME people you recruit are crap, in which case your recruitment is broken and you need to fix it, or–and this is more likely–there is institutional bias going on and you need to work out what it is and you need to stamp it out.“
- Writers of color are often pushed into the “literary” category, effectively distancing them from the mainstream and more lucrative genres. A survey of UK authors found that 42% of authors of color wrote literary fiction, by far the biggest genre for authors of color in the poll. By contrast, only 4% published in the crime and women’s commercial fiction genres, two genres that sell in far larger quantities than literary work. Diverse authors often felt that they were encouraged–or pushed–into the literary fiction genre. This means that authors of color are often at a commercial disadvantage, especially if they want to be full-time novelists.
- Authors of color in the UK feel pidgeonholed, too. One African Caribbean writer is quoted as saying, “There is a sense that if you are a Black writer, you should be writing about that–being Black. I have heard publishers say, ‘She’s Black, what is she doing writing about Australia?’” This is especially interesting because in the US, this phenomenon is often tied to the power of major ethnic-focused literary awards like the Coretta Scott King Award. But in the UK, without those awards, pidgeonholing of authors of color still happens.
- A primary problem for diverse graduates seeking careers in publishing is access to personal publishing contacts as well as paid internships. The biggest entries into publishing include having a contact in the industry and serving unpaid internships. As the study says, “It should be a matter of concern to the industry that a primary route into the business poses a significant barrier to those outside the affluent professional classes.“
- There are few people of color working in HR. People of color in UK publishing are most often employed in the editorial department (35%), finance department (35%), and in social media/online (35%). Only 4% of survey respondents said they had a person of color in their HR departments, which affects not only recruitment and retention but also general company culture.
- Diversity initiatives start up and then die again. Over the last decade, several programs have emerged to help recruit more diverse candidates for publishing jobs. However, many have petered out over lack of funding or leaders. What is required in order for these initiatives to be successful, the study suggests, is “management buy-in,” that is, a commitment from people at the senior level of publishers to sustaining these programs and committing the resources to do so.
You can read the full report here. While it is clear that the UK, like the US, has serious diversity problems, it’s nice to see such a comprehensive study on the state of their industry. What would it take to create something similar within the US? What groups would we want to see involved in an effort like this?
It’s also incumbent on all of us to ask ourselves: what does the UK now know that we still don’t know…and how can we find out?